Phone :
+ 86 018059983973Fax :
+86-595-22515221Email :
sales3@gester-instruments.comAdd :
7/F, No.15, Chifeng Road, Licheng Region, Quanzhou city of Fujian PR,China.Gester Instruments Co.,LTD. has been committed to the development and production of high-precision professional testing equipment. The mattress comprehensive tester launched by our company also reflects our company's persistent belief in the internationalization and professionalization of products. Below we will detail the two standards involved in the mattress testing equipment: some differences between EN 1957 2012 and ASTM F 1566 2014, so that our customers can choose the right tester for testing.
The Mattress Comprehensive Performance Tester was developed in accordance with the requirements of EN 1957 and ASTM F 1566. Durability tests, hardness ratings, height changes before and after testing, and load/displacement curves were also tested. The real-time observation of the graph and the derivation of each result are convenient for future reference and comparison.
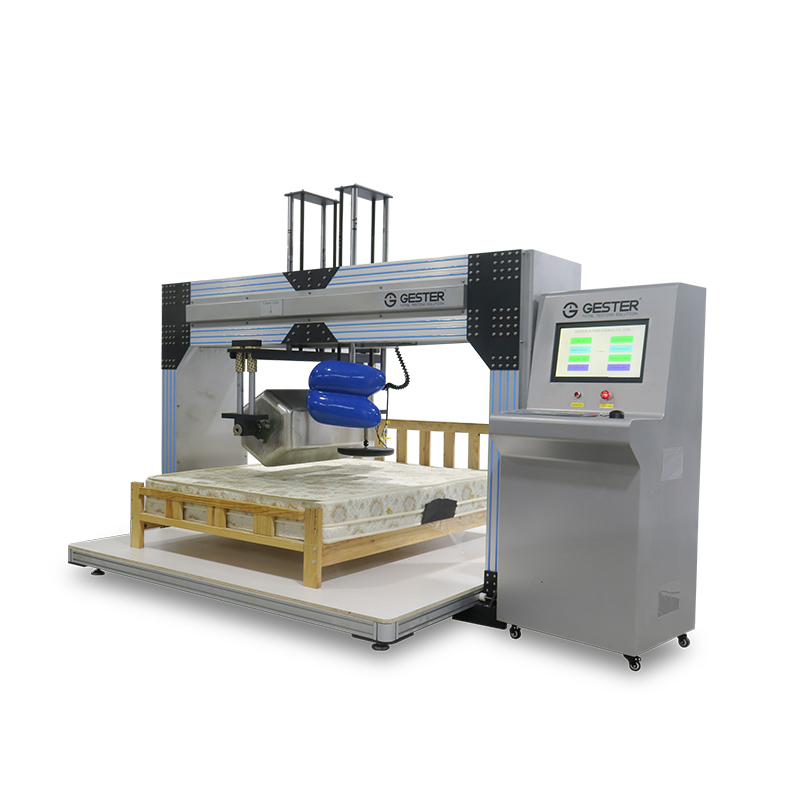 Let's start with the hardware. The durability test specified in the EN 1957 2012 standard is cylindrical in shape, and the ASTM F 1566 standard drum shape is hexagonal. The specific specifications are as shown:
Let's start with the hardware. The durability test specified in the EN 1957 2012 standard is cylindrical in shape, and the ASTM F 1566 standard drum shape is hexagonal. The specific specifications are as shown:
EN 1957 2012: length 1000 ± 2.5 mm, thickness 300 ± 5 mm, weight 1400N ± 7N (142.7 ± 0.7 Kg).
ASTM F 1566: 915 ± 76 mm in length, 432 ± 25 mm on the opposite side, weight 109 ± 4.5 kg.
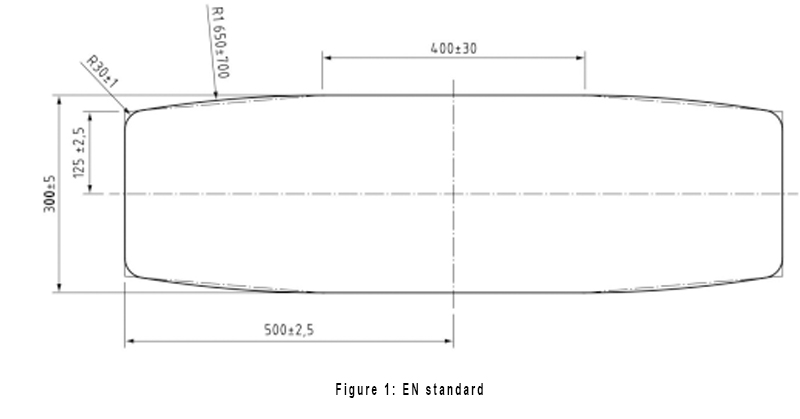
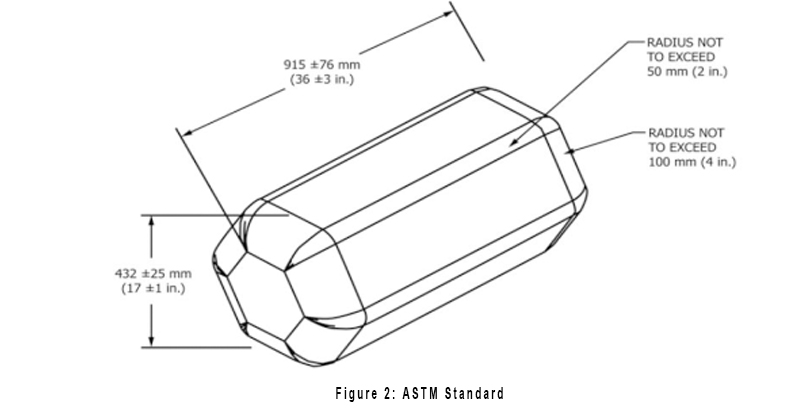
Due to the different shapes, the effect on the mattress is different during the test. The movement of the hexagonal roller of ASTM F 1566 is closer to the person who is lying on the bed to make the tumble motion, while the cylindrical shape is more able to detect the mattress. Spring structure durability.
There are also some differences in the hardness platen. The EN 1957 platen is a spherical surface with a radius of R 800 mm on the side that touches the mattress, and the side of the ASTM F 1566 platen that contacts the mattress is flat, the test procedure The force applied to the mattress is also different, 1000 N is specified in EN 1957 and 778 N is specified in ASTM F 1566.
Platen of EN 1957 2012: diameter 355 mm, the thickness is not clearly stated, we have a total thickness of 50 mm for the platen and a spherical radius of 800 mm for the contact mattress.
ASTM F 1566 platen: 344 ± 5 mm in diameter, 12 ± 1 mm thick, flat on both sides.
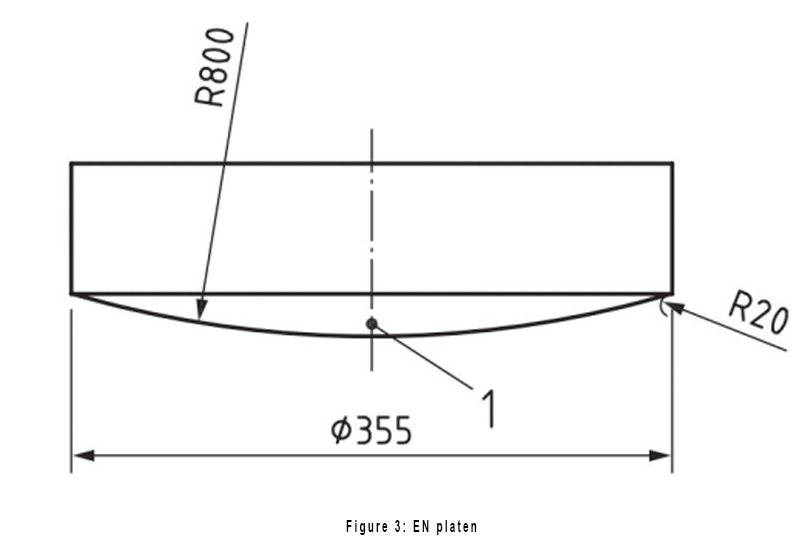
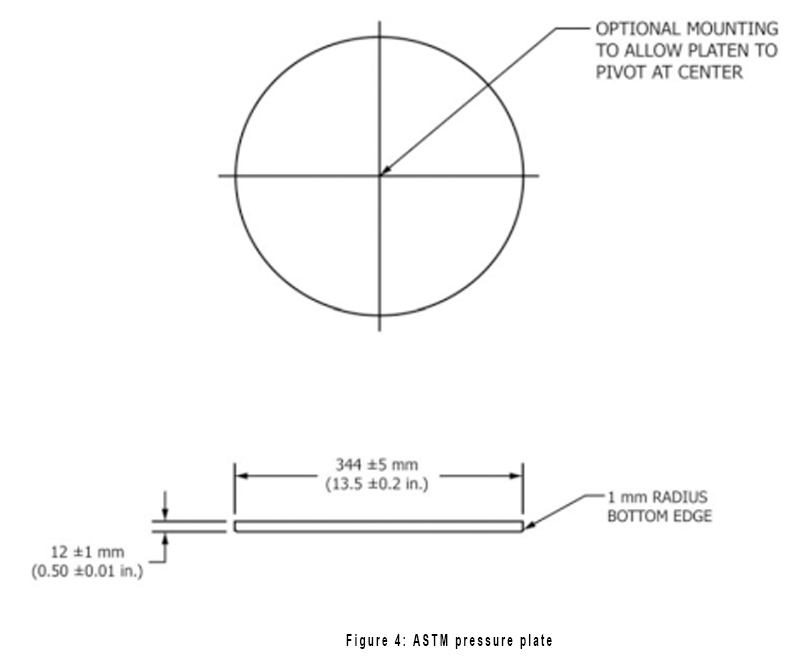
The test procedures are also different. We will introduce the test procedures in the two standards separately so that our customers have a clear understanding of the two standard test procedures.
Introduction to the mattress hardness test procedure of EN 1957 2012:
1. Adjustment: Place the mattress in a standard climate for one week before testing: 23 ° C, 50% humidity.
2. Remove the mattress from the standard climate and measure the height of the mattress within 5 minutes and record it. The measurement point is the center point and edge center of the mattress.
3. Perform durability test 100 times.
4. After the test is completed, it can be placed in a standard climate for 5 hours.
5.After 5.5 hours of adjustment, measure the height and hardness of the mattress after 100 durability tests and record it.
6. Perform 29,900 durability tests. (29,900 tests can be divided into two, the first part is called the intermediate number, the second part is called the total number, and the two parts are totaling 29900. When the first part: the middle number runs, the mattress needs to be measured and calculated once. The height, height change, hardness, hardness change, sturdy grade, and sturdy grade change are recorded and recorded. After the data is recorded, the second part: total durability test.)
7. After the test is completed, it can be placed in a standard climate for 5 hours.
8.After 8.5 hours of adjustment, the final results of the calculated height, hardness, and firm rating after 29,900 durability tests were compared and compared with the results of the initial 100 tests.
The specific recording method is as follows:
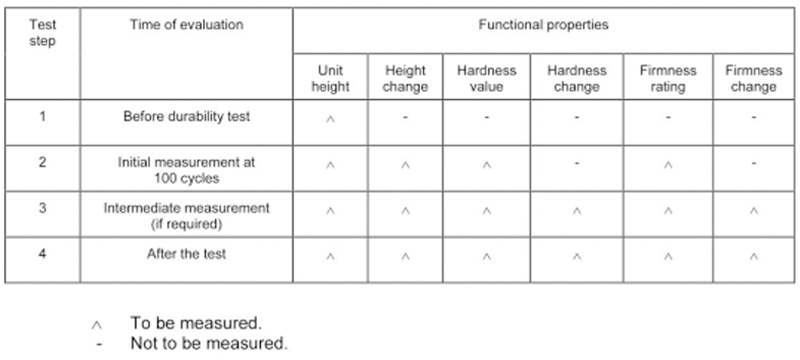
The above is the test procedure for the hardness of the upper surface of the mattress. The height loss test procedure for the edge of the bed is also specified in EN 1957:
1. Adjustment: Place the mattress in a standard climate for one week before testing: 23 ° C, 50% humidity
2. Remove the mattress from the standard climate, measure the height of the mattress within 5 minutes, and record it. The measurement point is the center point of the long side of the mattress.
3. Perform durability test 100 times
4. After the test is over, it can be placed in the standard climate for 5 hours.
5.After 5.5 hours of adjustment, the height of the mattress after 100 durability tests was measured and recorded.
6. Perform 4,900 durability tests.
7. After the test, it can be placed in the standard climate for 5 hours.
8.The height of the mattress after 4,900 durability tests was measured after 8.5 hours of adjustment and recorded.
9.Calculate the difference between the height of the initial 100 tests and the height of the 4,900 tests.
Then let's talk about the durability test and hardness test and the specific method of the firm rating:
The durability test is carried out by using a cylindrical roller to roll left and right on the mattress. The roller needs to be placed on the longitudinal axis of the mattress surface, that is, the center line of the mattress. Pressing the drum weight (1400N) on the mattress, reciprocating rolling about 16 times per minute, the unilateral stroke is 250mm, and the rolling distance from one end to the other is 500mm.
The hardness test is to apply a certain force value to the surface of the mattress through a circular platen, and record the load/displacement curve between 0 and 1000 N. The measurement method is as follows:
1. Preload the force to 1000N 3 times at the measuring point at a speed of 90mm/min, and the interval between loading 1000N at a time does not exceed 30s.
2. Measuring the hardness value within 30s after the third loading
3. The measurement data includes pairwise observations of load/displacement data up to 1000N. The recording point between 0 and 1000N is not less than 250 points, and the distance between the recorded points in the area of 0 to 450N does not exceed 2N.
4. When calculating the slope, take 5 points above each measurement point and 5 points below. Calculate the slope value by linear regression method.
This measurement process itself is a very complicated and precise job, and our mattress comprehensive tester is fully programmed to fully realize the load/displacement slope value through high-precision force and displacement sensors during the test. The load/displacement curve can be observed from time to time. After the test, the height, height difference, hardness, hardness difference, firm rating, strong rating difference can be directly displayed, and the result can be exported in the form of excel table.
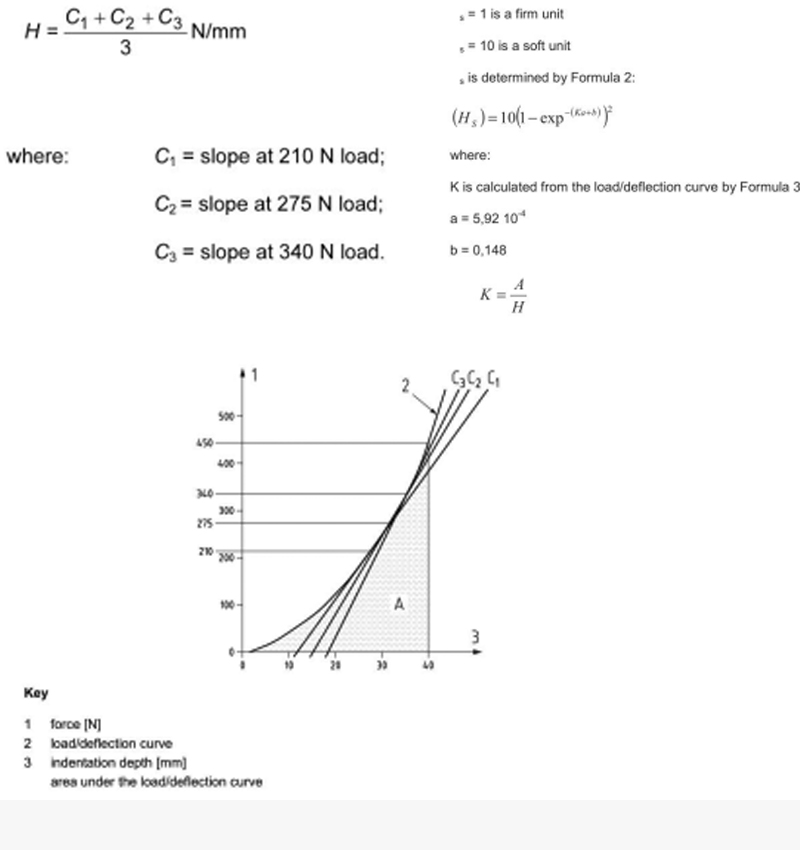
The height difference is obtained by comparing the height values of the mattress after 100 initial tests and the total number of tests, and the height is compared when the 50N is applied to the mattress. The hardness value is determined by the formula specified in EN 1957. The slope values of the three force points 210N, 275N, and 340N are recorded, and an average value is obtained, which is expressed in N/mm. The formula is shown in Fig. 5. . The sturdy rating itself is subjective data from the numbers 1 to 10, and the researchers have obtained a large number of subjective empirical data studies, which are derived from the formula given in EN 1957. The formula is shown in Fig. 6.
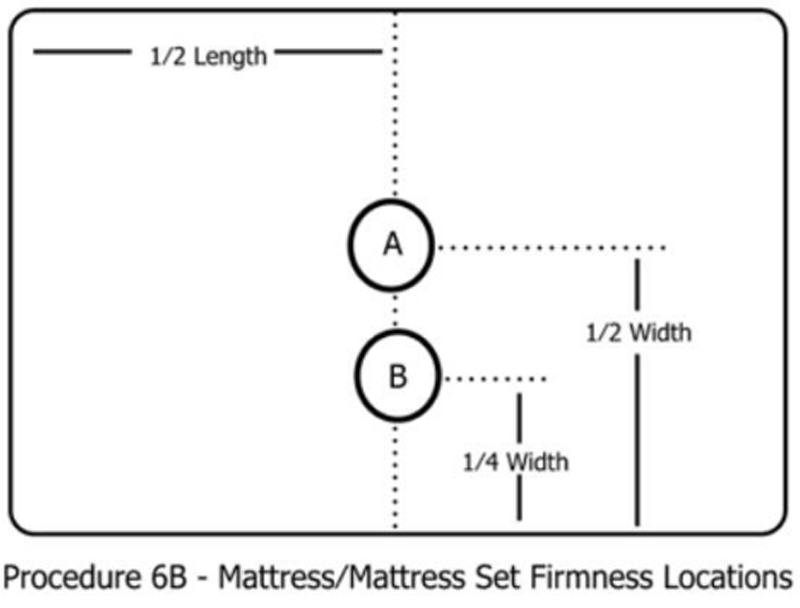
 Now we introduce the test procedure in the ASTM F 1566 standard. The procedure of ASTM F 1566 is simpler than the test procedure in the EN 1957 standard. The specific test position is used to reflect the tolerance of the mattress. The test point is shown in Figure 7:
Now we introduce the test procedure in the ASTM F 1566 standard. The procedure of ASTM F 1566 is simpler than the test procedure in the EN 1957 standard. The specific test position is used to reflect the tolerance of the mattress. The test point is shown in Figure 7:
1. Adjust and lay the mattress flat for at least 8 hours at an ambient temperature of 23 °C.
2. Measure the height and hardness of the mattress. The measuring points are A and B in Figure 7. Press the plate at the test point of A and B at a speed of 250mm/min until the platen is applied to the 778N on the mattress. Force, need to carry out 2 presses.
3. After preloading twice, the mattress can be rested for 6 minutes.
4. Press the plate at each test point and preload it to a force of 4.4 N to determine the reference point of the height of the mattress to facilitate calculation of the height difference after the test.
5. Start applying pressure to 778 N at a position of the reference point at a speed of 50 mm/min. And record the load/displacement data at intervals of 12.5 mm until it reaches 778N.
6. Record the amount of displacement at 778N.
7. Perform a durability test on the centerline of the mattress, 100,000.
8. Rest for 60 minutes after durability test.
9. Press the plate at a speed of 250 mm/min at the A and B test points until the platen exerts a force of 778 N on the mattress, requiring 2 presses.
10. After preloading twice, leave the mattress for 6 minutes.
11. Press the plate at each test point and preload it to a force of 4.4 N to determine the reference point of the mattress height to facilitate calculation of the height difference after the test.
12. At the position of the reference point, pressurize to 778 N at a speed of 50 mm/min. And record the load/displacement data at intervals of 12.5 mm until it reaches 778N.
13. Record the amount of displacement at 778N.
14. Comparison of hardness value difference and height difference before and after durability test.
The hardness value is determined by dividing 778N by the amount of displacement at 778 N, in N/mm, and the load/displacement data curve also reflects the spring rate at the bottom of the bed.
In the durability test, the maximum stroke of the drum is the width of the mattress minus the width of one flat side of the hexagonal drum. The minimum stroke must not be less than 70% of the width of the mattress or 965mm, whichever is smaller. The test frequency is 20 reciprocations per minute.
The above is the relevant content of EN 1957 and ASTM F 1566 on the hardness evaluation of mattresses. We finally compare each test method in the two standards so that we can see the difference more intuitively.
Durability test:
EN 1957: Cylindrical roller. With a single stroke of 250mm, the total stroke is 500mm. The speed of 16 reciprocating speeds per minute rolls on the mattress.
ASTM F 1566: Hexagonal roller with a maximum stroke (the width of the mattress minus the width of one of the sides of the hexagonal roller) or a minimum stroke of 965 mm or a minimum stroke (70% of the width of the mattress), with a smaller quasi. Speed 20 reciprocating speeds per minute to roll on the mattress.
Determination of hardness value:
EN 1957: Hardness plate is pressed to 1000N. Obtain 210N, 275N, 340N when the pressure plate is pressed. The load/displacement values of the three points are taken as the average value, which is the hardness value.
ASTM F 1566: The hardness disk is pressed to 778N. Apply a force of 4.4 N to the mattress with a pressure plate, and use this point as a reference point to continue pressing down to 778 N to obtain the displacement value. The 778N divided by the displacement value at that time is the hardness value.
Height determination:
EN 1957: Used as a reference point when a pressure plate is applied to the mattress at 50N.
ASTM F 1566: Used as a reference point when a platen is applied to the mattress at 4.4 N.
Rugged rating:
EN 1957: A subjectively developed formula to obtain a number between 1 and 10 to assess the firmness of the mattress.
ASTM F 1566: If the solid rating is not measured in the same way, it is not described here.

I believe that after comparing, we have found the difference between the two standards, and GESTER has developed two mattress testing machine products for the difference between the two standards, so that our customers can make choices. All our efforts are to make Customers have better and more professional testing instruments, and the choice of customers is also a kind of recognition for us. We will always give Jester a longer-term and more recognition by providing professional technical support to customers. Let GESTER become the best choice in the testing industry, as the industry leader continues to open up a new future.